Custom Url Picker
Overview
The picker that allows you to select a list of values retrieved from an external Microservice.
Configuration
The following configuration must be set in order to start using the CustomUrlPicker:
tags:
title: Tags
type: array
description: a field implementing Custom URL picker
ui:field: CustomUrlPicker
ui:options:
maxNumberToSelect: 3
allowArbitraryValues: true
selectedField: value
ui:fieldsToSave:
- id
- value
- description
ui:displayFields:
- value
ui:apiSpec:
retrieval:
microserviceId: 'mocked-microservice-id'
baseUrl: http://url.com // OPTIONAL
path: /some/path // OPTIONAL
method: POST // OPTIONAL
params:
limit: 5
areaType: 'marketing'
validation:
microserviceId: 'mocked-microservice-id'
baseUrl: http://url.com // OPTIONAL
path: /some/path // OPTIONAL
method: POST // OPTIONAL
The ui:options property can contain three possible values: maxNumberToSelect, allowArbitraryValues and selectedField. The first one is optional, this means that if not provided the Custom URL Picker enables users to select how many values they want, otherwise it limit the number of item that a user can select to the maxNumberToSelect number. The second one
is optional and has a default value to false. If true, it enables users to type arbitrary strings inside the picker and press Enter to confirm the value. The third one is used to select the selected object's field to visualize inside the picker (as showed below).
If allowArbitraryValues is true and the maxNumberToSelect is defined, the user can add as many values it wants until the maxNumberToSelect value is reached.
If allowArbitraryValues is true, the Custom URL Picker will not perform any validation on the selected values.
The ui:fieldsToSave property is used to select the value's attributes that we want to save in the catalog-info.yaml file. It is an optional field and in case it is missing, the value's attributes to save are considered the ones under ui:displayFields (see the section below).
The only mandatory field to insert under ui:fieldsToSave is the id otherwise the Custom URL Picker cannot render correctly the option selected and, also, it cannot perform correctly the validation.
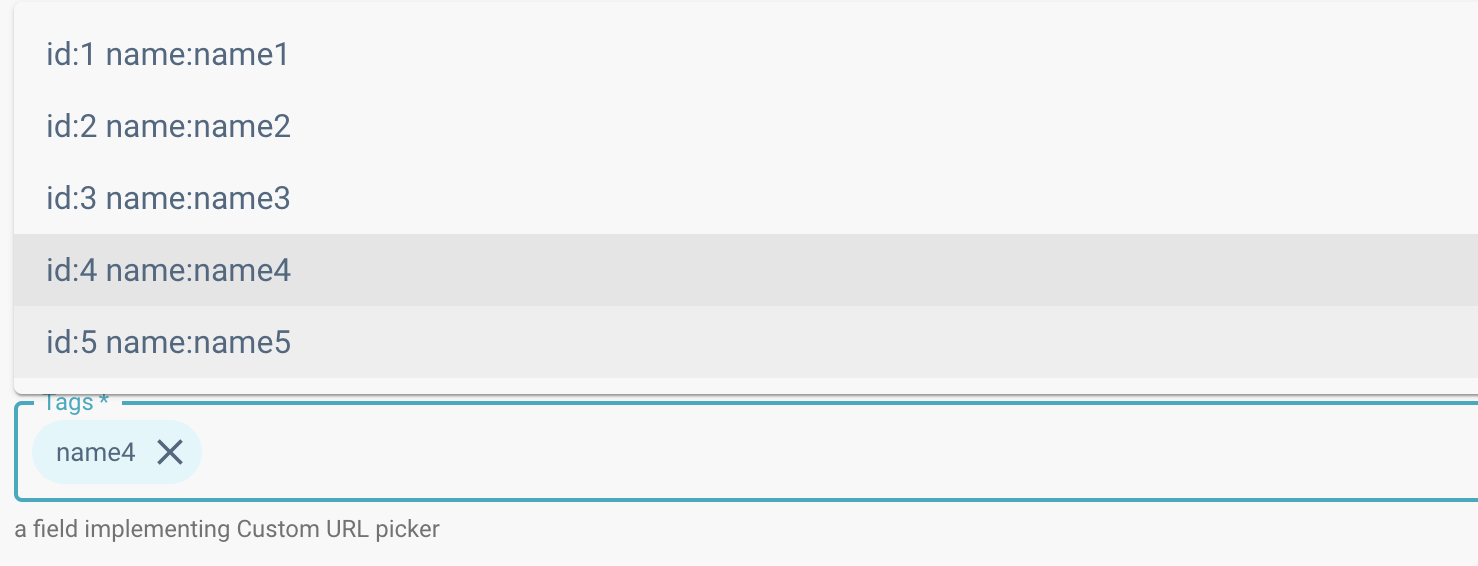
The ui:displayFields property is used to select the returned object fields to visualize in the drop-down list of the picker (as showed below).
The ui:displayFields property must be a sub-set of the ui:fieldsToSave property. For example, if there are id, value and description under ui:fieldsToSave and name under ui:displayFields, the following error will be shown:

The ui:options.selectedField property should also be included in the ui:displayFields property.
The ui:apiSpec property is an object that contains the API specifications to which the Picker will send the requests for the two phases of the Custom URL Picker: retrieval and validation. The first one is executed only when the creation wizard is opened, while the second one is executed when the edit wizard is opened or before deploying a data product descriptor in order to see if the picker contains the right data. The object for retrieval and validation is composed by the following fields:
microserviceId: an identifier that will be used to take the API key that will be set in the Witboost configuration filebaseUrl: an optional field defining the URL used to perform an HTTP callpath: an optional field defining the path used to perform the HTTP requestmethod: an optional field defining the method used to perform the HTTP requestparams: an optional object that will be put in the body of the request. It can contain static fields like the one showed in the above example or dynamic fields (see the Dynamic Field section). Theparamsfield can contain also the limit parameter that defines the number of values that the Custom URL Picker will receive for each request to the Microservice. It is an optional field and the default (and minimum) value is 5. This parameter will also be passed to the body of the validation API asqueryParametersproperty. This is because the validation API needs the same body of the retrieval in order to perform its operation.
The baseUrl, path and method parameters are optional, i.e. when a user defines them, they will overwrites the one that are inside the Witboost configurations.
The params parameter should contain also the "limit" that cannot be less than 5. In case you do not put anything in there, the limit will have default value 5.
Do not put a value less than 5 for limit parameter.
Infinite scrolling mechanism
The CustomURLPicker incorporates a feature that enables pagination of microservice results through an infinite scrolling mechanism. This mechanism utilizes a query parameter named "offset," which represents a numeric value. For instance, suppose a user is browsing a list of items retrieved from the microservice. As they reach the end of the current list, the "offset" parameter is updated to skip the already fetched elements and fetch the next batch.
Let's consider an example:
Initially, the user loads the page and the offset parameter is set to 0. The microservice returns the first batch of items, say 10 elements (set by the limit value), based on this offset value. As the user scrolls down and reaches the end of the drop-down list, the offset parameter is set to 10, to skip the 10 elements already fetched. Subsequently, the microservice retrieves the next 10 elements starting from the index specified by the updated offset value (in this case, 10).
This process continues as the user scrolls further, with the offset parameter incrementing each time and the microservice fetching the subsequent batch of items accordingly. The Custom URL Picker seamlessly appends these newly retrieved elements to the existing ones, providing a continuous and uninterrupted browsing experience for the user.
The Custom URL Picker does not know anything regarding how many values the external microservice will return. It will just increase the offset number and append the microservice results to the existing ones. The microservice will compute the values to return to the Custom URL Picker by considering the offset mechanism described above.
Dynamic fields
The Custom Url Picker enables users to put under ui:apiSpec.retrieval.params property, some fields that have some special value chars: ${{ fieldName }}. This means that a user can put the value for that field to the one that is inside the "fieldName" field in the same template. For example, the following template.yaml file contains two fields email and tags. The user has defined an emailValue property under params with the special characters described above. The Custom URL Picker will take the value that the builder user will put in the email field of the template and put that value in the emailValue field.
email:
title: Contact email
type: string
format: email
description: Point of contact, it could be the owner or a distribution list, but must be reliable and responsive
tags:
title: Tags
type: array
description: a field implementing Custom URL picker
ui:field: CustomUrlPicker
ui:options:
allowArbitraryValues: true
selectedField: name
ui:displayFields:
- id
- name
ui:apiSpec:
retrieval:
microserviceId: 'mocked-microservice-id'
params:
limit: 5
areaType: 'marketing'
emailValue: ${{ email }}
validation:
microserviceId: 'mocked-microservice-id'
The user can use dynamic fields in multiple ways:
- In a nested object property:
params:
limit: 5
areaType: 'marketing'
emailValue:
name: ${{ email }}
domain: agilelab.it
- In an array:
params:
limit: 5
areaType: 'marketing'
emailValue: ['${{ email }}', 'name.surname@company.it']
- In both of them:
params:
limit: 5
areaType: 'marketing'
emailValue:
values: ['${{ email }}', name.surname@company.it]
domain: agilelab.it
It is possible to put in the special characters only the field names that are in the same step of the Custom URL picker.
When a dependent field changes, the custom URL picker will be reset.
If the dynamic field cannot be resolved, a warning will be displayed: The dynamic field "${fieldName}" is empty or wrong. It will be skipped from the request body.. So make sure to reference the correct field name.
Avoid to put another Custom URL Picker which depends from yours as dynamic field (cyclic dependency) in order to avoid unexpected results.
Avoid to put the Custom URL Picker itself as a dynamic field in order to avoid unexpected results.
Witboost configuration
In order to use the Custom URL Picker we need to define some configuration properties inside Witboost values.yaml file under ui.appConfig.mesh.builder.scaffolder section.
ui:
mesh:
builder:
scaffolder:
microserviceConfiguration:
- microserviceId: microservice-id
baseUrl: https://someuri.com
retrievalPath: /some/retrieval/path // OPTIONAL
validationPath: /some/validation/path // OPTIONAL
retrievalMethod: POST // OPTIONAL
validationMethod: POST // OPTIONAL
apiKey: api_key_value // OPTIONAL
The fields microserviceId and baseUrl are mandatory while apiKey, retrievalPath, validationPath, retrievalMethod, validationMethod are optional and can be put in there only the Microservice wants to expose API with different paths and methods. For what concern the apiKey configuration, this will be set only if the Microservice requires some authenticated requests (in this case the value of apiKey will be set in the header parameter X-API-Key).
The baseUrl, retrievalPath, validationPath, retrievalMethod, validationMethod fields can be overwritten by putting the same parameters in the template.yaml file, under ui:apiSpec.retrieval or ui:apiSpec.validation.
The retrievalPath and validationPath configurations must start with '/' to avoid unexpected behaviours.
Microservice APIs
In order to make the microservice compatible with the Custom URL Picker specifications, it must implement two APIs: POST v1/resources and POST v1/resources/validate. These APIs must be compliant to the corresponding Open API specification.
The API paths (v1/resources and v1/resources/validate) can be changed as you want. If you do that, remember to change their references under ui.appConfig.mesh.builder.scaffodler.microserviceConfiguration.retrievalPath and ui.appConfig.mesh.builder.scaffolder.microserviceConfiguration.validationPath if you are defining the API in the configuration, or under ui:apiSpec.retrieval.path and ui:apiSpec.validation.path if you are defining the API in the templates.
Enable Witty Autocomplete
You can enable AI-powered suggestions in the Custom Url picker by setting smartSuggestions.enabled = true. For a full example and more details, see the Witty Autocomplete Agent.